User Manual
Contents
Overview
The Enrichment Map Cytoscape Plugin allows you to visualize the results of gene-set enrichment as a network. It will operate on any generic enrichment results as well as specifically on Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) results. Nodes represent gene-sets and edges represent mutual overlap; in this way, highly redundant gene-sets are grouped together as clusters, dramatically improving the capability to navigate and interpret enrichment results.
Gene-set enrichment is a data analysis technique taking as input
a (ranked) gene list, from a genomic experiment
- gene-sets, grouping genes on the basis of a-priori knowledge (e.g. Gene Ontology) or experimental data (e.g. co-expression modules)
and generating as output the list of enriched gene-sets, i.e. best sets that summarizing the gene-list. It is common to refer to gene-set enrichment as functional enrichment because functional categories (e.g. Gene Ontology) are commonly used as gene-sets.
Installation
The Enrichment Map Plugin requires Cytoscape Version 2.6.x. If you don't have Cytoscape or an older Version (2.5 or older), please download the latest Release from http://www.cytoscape.org/ and install it on your computer.
Download the Enrichment Map plugin from Software/EnrichmentMap and manually place the file EnrichmentMap.jar in the Cytoscape/plugins folder.
Quick Start Guide
Creating an Enrichment Map
You have two main options:
- Load GSEA Results
- Load Generic Results
The only difference between the two modes is the structure of the enrichment table(s). In either case, to use the plugin you will need the following files:
- file.gmt: gene-set to gene ID
- file.txt or .gct: expression matrix
- file.txt or .xls (*): enrichment table(s)
(*) GSEA saves the enrichment table as a .xls file; however, these are not true Excel files, they are tab-separated text files with a modified extension; Enrichment Map does not work with "true" Excel .xls files.
If your enrichment results were generated from GSEA, you will just have to pick the right files from your results folder. If you have generated the enrichment results using another method, you will have to go to the Full User Guide, File Format section, and make sure that the file format complies with Enrichment Map requirements.
You can use the parameter defaults. For a more careful choice of the parameter settings, please go to the Full User Guide, Tips on Parameter Choice.
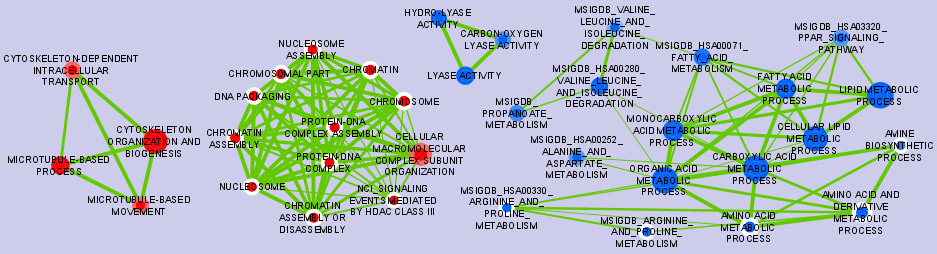
Graphical Mapping of Enrichment
- Nodes represent gene-sets.
- Edges represent mutual overlap.
- Enrichment significance (p-value) is conveyed as node color intensity.
The enriched phenotype is conveyed by node color hue.
Note: In standard two-class designs, where two phenotypes are comared (e.g. treated vs untreated) the color hue conveys the enriched phenotype; this is equivalent to mapping enrichment in up- and down-regulated genes, if one of the two phenotypes is assumed as reference (e.g. untreated), and the other phenotype is the one of interest; in such a case, enriched in the phenotype of interest means up, and enrichment in the reference phenotype means down.
- Node size represents how many genes are in the gene-set.
Exploring the Enrichment Map
- The “Parameters” tab in the “Results Panel” on the right side of the window contains a legend mapping the colours to the phenotypes and displaying the parameters used to create the map (cut-off values and data files).
- The “Network” tab in the “Control Panel” on the left lists all available networks in the current session and at the bottom has a overview of the current network which allows to easily navigate in a network even at higher zoom levels by dragging the blue rectangle (the current view) over the network.
- Clicking on a node (the circle that represents a gene set) will open the “EM Geneset Expression Viewer” tab in the “Data Panel” showing a heatmap of the expression values of all genes in the selected gene set.
- Clicking on an edge (the line between two nodes) will open the “EM Overlap Expression Viewer” tab in the “Data Panel” showing a heatmap of the expression values of all genes both gene sets that are connected by this edge have in common.
- If several nodes and edges are selected (e.g. by dragging a selection box around the desired gene sets) the “EM Geneset Expression Viewer” will show the union of all genes in the selected gene sets and the “EM Overlap Expression Viewer” will show only those genes that all selected gene sets have in common.
- The “Geneset Summary” tab in the “Results Panel” on the right contains information about which nodes and edges are selected.
Advanced tips
- With large networks and low zoom-levels Cytoscape automatically reduces the details (such as hiding the node labels and not showing the node borders). To override this mechanism click on “View / Show Graphics Details”
The VizMapper and the Node- and Edge Attribute Browser open up a lot more visualization options like linking the label size to Enrichment Scores or p-values. Refer to the Cytoscape manual at www.cytoscape.org for more information.
If you have used Genesets from GSEAs MSigDb, you can access additional informations for each gene set, by adding the a new property:
(Edit / Preferences / Properties... / Add -> enter property name: nodelinkouturl.MSigDb -> enter property value: http://www.broad.mit.edu/gsea/msigdb/cards/%ID%.html -> [
 ] Make Current Cytoscape Properties default -> (OK) ). Now you can right-click on a node and choose LinkOut/MSigDb to open the Database entry of the Geneset represented by that node in your Browser.
] Make Current Cytoscape Properties default -> (OK) ). Now you can right-click on a node and choose LinkOut/MSigDb to open the Database entry of the Geneset represented by that node in your Browser.
Full User Guide
File Formats
Gene sets file (GMT file)
- The gene set file describes the genesets used for the analysis. These files can be obtained
directly downloading gene-sets collected in the MSigDB
- Note: if you use MSigDB Gene Ontology gene-sets, please consider that they do not include all annoations, as an evidence code filter is applied; if you are interested in achieving maximum coverage, download the original annotations
converting gene annotations / pathways from public databases
Note: if you are a R user, Bioconductor offers annotation packages such as GO.db, org.Hs.eg.db, KEGG.db
- Each row of the geneset file represents one geneset and consists of:
- geneset name (--tab--) description (--tab--) a list of tab-delimited genes that are part of that geneset.
- The geneset names must be unique.
Expression Data file (GCT, TXT or RNK file)
- The expression data can be loaded in three different formats: gct, rnk or txt.
Gct differs from txt only because two additional lines are required at the top part of the file.
Rnk file is completely different from the GCT or TXT file. It represents a ranked list of genes containing only gene name and a rank or score.
- Each line of expression file contains a:
- name (--tab--) description (--tab--) followed by a list of tab delimited expression values.
- OR name (--tab--) rank or score
- The first line in the txt file and third line in the gct file consists of column headings.
- The GCT file contains two additional lines at the top of the file.
- The first line contains #1.2.
- The second line contains the number of data rows (tab) the number of data columns.
If the GCT file contains Probeset ID's as primary keys (e.g. as you had GSEA collapse your data file to gene symbols) you need to convert the gct file to use the same primary key as used in the gene sets file (GMT file). Until this Feature is implemented in the EnrichmentMapPlugin, his can be done with the Python script replace_probeSetIDs.py using the Chip platform file that was used by GSEA.
$ replace_probeSetIDs.py -h
Usage: replace_probeSetIDs.py [options] -i input.gct -o output.gct -c platform.chip
Options:
--version show program's version number and exit
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i FILE, --input=FILE
input .gct file
-o FILE, --output=FILE
output .gct file
-c FILE, --chip=FILE Chip File
--collapse Collapse multiple probesets for the same gene symbol
(max_probe)
--no-collapse Don't collapse multiple probesets (default)
Enrichment Results files
GSEA result files
- For each analysis GSEA produces two output files. One representing the enriched genesets in phenotype A and the other representing the enriched genesets in phenotype B.
- These files are usually named "gsea_report_for_phenotypeA.Gsea.########.xls" and "gsea_report_for_phenotypeB.Gsea.########.xls"
- The files should be loaded in as is and require no pre-processing.
- There is no need to worry about which Enrichment Results Text box to put the two files. The phenotype is specified by the sign of the ES score and is computed internally by the program.
Generic results files
- The generic results file is a tab delimited file with enriched gene-sets and their corresponding p-values (and optionally, FDR corrections)
- The Generic Enrichment Results file needs:
- gene-set ID (must match the gene-set ID in the GMT file),
- gene-set name or description,
- p-value,
- FDR correction value
- Phenotype: +1 or -1, to identify enrichment in up- and down-regulation, or, more in general, in either of the two phenotypes being compared in the two-class analysis
- +1 maps to red
- -1 maps to blue
Notes:
- description and FDR columns can have empty or NA values, but the column and the column header must exist
- if no value is provided under phenotype, Enrichment Map will assume there is only one phenotype, and will map enrichment p-values to red
Additional Information on GSEA File Formats
Additional Information on GSEA File Formats can be found here
RPT files
- A special trick for GSEA results, in any GSEA analysis an rpt file is created that specifies the location of all files (including the gmt, gct, results files, phenotype specification, and rank files).
- Any of the Fields under the dataset tab (Expression, Enrichment Results 1 or Enrichment Results 2) will accept an rpt file and populate GMT, Expression, Enrichment Results 1, Enrichment Results 2, Phenotypes, and Ranks the values for that dataset.
- A second rpt file can be loaded for dataset 2. It will fail if the GMT file specified is different than the one specified in dataset 1.
Advanced Settings
- For each dataset there are additional parameters that the user can set but are not required.
- The advanced parameters include:
- Phenotypes (phenotype1 versus phenotype2)
- Rank file - file specifying the ranks of the genes in the analysis
- This file has the format specified in the above section - gene (--tab--) rank or score.
- By default the phenotypes are set to Up and Down but in the advanced setting mode the user can change these to any desired text.
- Both of these fields are populated when the user loads the input files using the rpt option.
Tips on Parameter Choice
P-value and FDR Thresholds
Here are different sets of thresholds you may consider for GSEA:
- Very permissive:
p-value < 0.05
FDR < 0.25
- Moderately permissive:
p-value < 0.01
FDR < 0.1
- Moderately conservative:
p-value < 0.005
FDR < 0.075
- Conservative:
p-value < 0.001
FDR < 0.05
We recommend to use permissive thresholds only if your having a hard time finding any enriched terms. For high quality, high coverage transcriptomic data, the number of enriched terms at the very conservative threshold is usually 100-250.
Jaccard vs. Overlap Coefficient
- The Overlap Coefficient is recommended when relations are expected to occur between large-size and small-size gene-sets, as in the case of the Gene Ontology.
- The Jaccard Coefficient is recommended in the opposite case.
- When the gene-sets are about the same size, Jaccard is about the half of the Overlap Coefficient for gene-set pairs with a small intersection, whereas it is about the same as the Overlap Coefficient for gene-sets with large intersections.
- When using the Overlap Coefficient generates a the map with several large gene-sets overly connected to many other gene-sets, we recommend switching to the Jaccard Coefficient.
Overlap Thresholds
- 0.5 is moderately conservative, and is recommended for most of the analyses.
- 0.3 is permissive, and might result in a messier map.
Jaccard Thresholds
- 0.5 is very conservative
- 0.25 is moderately conservative
The Input Panel
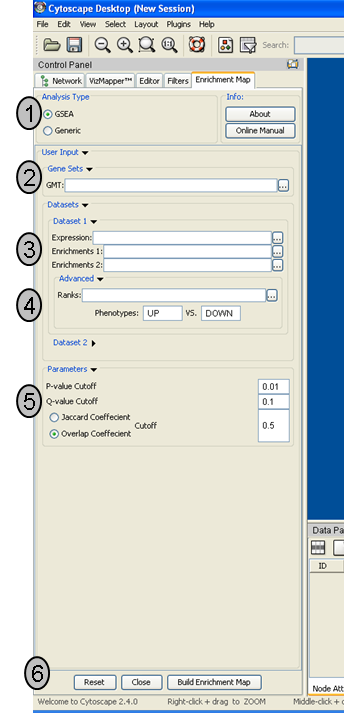
Analysis Type
- There are two distinct types of Enrichment map analyses, GSEA or Generic.
GSEA - takes as inputs the output files created in a GSEA analysis. File formats are specific to files created by GSEA. The main difference between this and generic is the number and format of the Enrichment results files. GSEA analysis always has two enrichment results files, one for each of the phenotypes compared.
Generic - takes as inputs the same file formats as a GSEA analysis except the Enrichment results file is a different format and there is only one enrichment file. Generic File description
- There are two distinct types of Enrichment map analyses, GSEA or Generic.
Genesets - path to gmt file describing genesets. User can browse hard drive to find file by pressing ... button.
Dataset 1 - User can specify expression and enrichment files or alternatively, an rpt file which will populate all the fields in genesets,dataset # and advanced sections.
Advanced - Initially collapsed (expand by clicking on arrow head directly next to Advanced), users have the option of modifying the phenotype labels or loading gene rank files.
Parameters - User can specify p-value, fdr and overlap/jaccard cutoffs. Choosing Optimal parameter values
Actions - The user has three choices, Reset (clears input panel), Close (closes input panel), and Build Enrichment map (takes all parameters in panel and builds an Enrichment map)
The Data Panel
- The bottom (south) panel.
Expression Viewer
- There are two different types of Expression Viewers, each is represnted as a separate tab in data panel:
- EM Overlap - shows the expression of genes in the overlap (intersection) of all the genesets selected
- EM Geneset - shows the expression of genes of the union of all the genesets selected.
- Features of the Expression Viewer include:
- Normalization
- Data as is - represents the data as it was loaded
- Row Normalize Data - for each value in a row of expression the mean of the row is subtracted followed by division by the row's standard deviation.
- Log Transform Data - takes the log of each expression value
- Sorting
- Hierarchical cluster - as computed using pearson correlation of the entire expession set.
- If rank files for the data sets are provided at input they will show up as 'Dataset 1 Ranking' and 'Dataset 2 Ranking' and by selecting them the user will be able to sort the expression accordingly
- if an expression value does not have a corresponding rank in the ranking file its expression does not appear in the heatmap.
Add Ranking ... - allows user to upload an additional rank file (in the appropriate format,as outlined in Rank file descriptions). There is no limit on the number of rank files that are uploaded. The user is required to give a name to the rank file.
- Save Expression Set
- The user can save the subset of expression values currently being viewed in the expression viewer as txt file.
- Normalization
Node Attributes
- For each Enrichment map created the following attributes are created for each node:
- EM#_Name - the gene set name
EM#_Formatted_name - a wrapped version of the gene set name so it is easy to visualize.
Note: This is the default label of the node but some users find it easier to arrange the network when the name is not wrapped. If this is the case in the vizmapper the user can switch the label mapping from EM#_formatted_name to EM#_name.
- EM#_GS_DESCR - the gene set description (as specified in the second column of the gmt file)
- EM#_Genes - the list of genes that are part of this gene set.
- Additionally there are attributes created for each dataset (a different set for each dataset if using two dataset mode):
- EM#_pvalue_dataset(1 or 2) - Gene set p-value, as specified in GSEA enrichment result file.
- EM#_qvalue_dataset(1 or 2) - Gene set q-value, as specified in GSEA enrichment result file.
- EM#_Colouring_dataset(1 or 2) - Enrcihment map parameter calculated using the formulat 1-pvalue multiplied by the sign of the ES score (if using GSEA mode) or the phenotype (if using the Generic mode)
- GSEA specific attributes (these attributes are not populated when creating an enrichment map using the generic mode)
- EM#_ES_dataset(1 or 2) - Enrcihment score, as specified in GSEA enrichment result file.
- EM#_NS_dataset(1 or 2) - Normalized Enrcihment score, as specified in GSEA enrichment result file.
- EM#_fwer_dataset(1 or 2) - Family-wise error score, as specified in GSEA enrichment result file.
Edge Attributes
- For each Enrichment map created the following attributes are created for each edge:
- EM#_Overlap_size - the number of genes associated with the overlap of the two genesets that this edge connects.
- EM#_Overlap_genes - the names of the genes that are associated with the overlap of the two genesets that this edge connects.
EM#_similarity_coeffecient - the calculated coeffecient for this edge.
The Results Panel
- The right (east) panel
Parameters pane
- Reference panel containing legends, slider bars for the user to modify p-value and q-value cut-offs, parameters used for the analysis